|
Code of Federal Regulations (Last Updated: November 8, 2024) |
 |
Title 49 - Transportation |
 |
Subtitle B - Other Regulations Relating to Transportation |
 |
Chapter V - National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, Department of Transportation |
 |
Part 571 - Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards |
 |
Subpart B - Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards |
§ 571.403 - Standard No. 403; Platform lift systems for motor vehicles.
-
§ 571.403 Standard No. 403; Platform lift systems for motor vehicles.
S1. Scope. This standard specifies requirements for platform lifts used to assist persons with limited mobility in entering or leaving a vehicle.
S2. Purpose. The purpose of this standard is to prevent injuries and fatalities to passengers and bystanders during the operation of platform lifts installed in motor vehicles.
S3 Application. This standard applies to platform lifts manufactured on and after April 1, 2005, that are designed to carry standing passengers, who may be aided by canes or walkers, as well as persons seated in wheelchairs, scooters, and other mobility aids, into and out of motor vehicles.
S4. Definitions.
Bridging device means that portion of a platform lift that provides a transitional surface between the platform surface and the surface of the vehicle floor within the platform threshold area.
Cycle means deploying a platform lift from a stowed position, lowering the lift to the ground level loading position, raising the lift to the vehicle floor loading position, and stowing the lift. The term includes operation of any wheelchair retention device, bridging device, and inner roll stop.
Deploy means with respect to a platform, its movement from a stowed position to an extended position or, one of the two loading positions. With respect to a wheelchair retention device or inner roll stop, the term means the movement of the device or stop to a fully functional position intended to prevent a passenger from disembarking the platform or being pinched between the platform and vehicle.
Floor reference plane means the plane perpendicular to the longitudinal vehicle reference plane for platform lifts that deploy from the side of the vehicle or perpendicular to the transverse vehicle reference plane for platform lifts that deploy from the rear of the vehicle, and tangent to the outermost edge of the vehicle floor surface adjacent to the lift platform. (See figure 1.)
Gap means a discontinuity in a plane surface, or between two adjacent surfaces.
Inner roll-stop means a device that is located at the edge of the platform that a passenger or mobility aid must traverse when entering and exiting the platform from the vehicle floor loading position and that is designed to retain mobility aids on the platform surface during the range of passenger operation.
Lift reference plane means the plane that is defined by two orthogonal axes passing through the geometric center of the platform surface of a platform lift. One axis is perpendicular to the platform reference plane and the other is parallel to the direction of wheelchair travel during loading of the lift. (See figure 1.)
Loading position means, with respect to a platform lift, a position at which a passenger can either embark or disembark the lift. The two loading positions are at vehicle floor and ground level.
Longitudinal vehicle reference plane means the plane that is perpendicular to the floor reference plane and contains the longitudinal axis of the vehicle when the vehicle body is level and moves along with the vehicle body in response to the loading of the vehicle suspension. (See figure 1.)
Outer barrier is a particular wheelchair retention device that is located on the edge of the platform, is traversed during ground level loading and unloading, and is designed to retain wheelchairs on the platform surface during the range of passenger operation.
Platform means that portion of a platform lift on which the mobility aid or passenger rests while being raised or lowered.
Platform lift means a level change device, including any integration of existing vehicle components, and excluding a ramp, used to assist persons with limited mobility in entering or leaving a vehicle.
Platform reference plane means a plane tangent to the platform surface at its geometric center. (See figure 1.)
Platform surface means the passenger-carrying surface of the lift platform.
Platform threshold area means the rectangular area of the vehicle floor defined by moving a line that lies on the portion of the edge of the vehicle floor directly adjacent to the platform, through a distance of 457 mm (18 inches) across the vehicle floor in a direction perpendicular to the edge. Any portion of a bridging device that lies on this area must be considered part of that area.
Private use lift means a platform lift certified to the requirements for private use lifts and requirements in this standard for all lifts.
Public use lift means a platform lift certified to the requirements for public use lifts and requirements in this standard for all lifts.
Range of passenger operation means the portion of the lift cycle during which the platform is at or between the vehicle floor and ground level loading positions excluding any stow and deploy operations.
Standard test load means a static load or mass centered on the test pallet such that the total combined mass for public-use lifts shall be 272 kg (600 lb), and the total combined mass for private-use lifts shall be the lift manufacturer's stated rated load or 181 kg (400 lb), whichever is greater.
Stow means with respect to a platform, its movement from a position within the range of passenger operation to the position maintained during normal vehicle travel; and, with respect to a wheelchair retention device, bridging device, or inner-roll stop, its movement from a fully functional position to a position maintained during normal vehicle travel.
Test pallet means a platform on which required test loads are placed for handling and moving.
Transverse vehicle reference plane means the plane that is perpendicular to the floor reference plane and contains the transverse axis of the vehicle when the vehicle body is level and that moves along with the vehicle body in response to the loading of the vehicle suspension. (See figure 1.)
Wheelchair retention device means a device designed to prevent wheelchairs from leaving the edge of the platform used for ground level loading and unloading during the range of passenger operation.
S5. [Reserved]
S6. Requirements.
(a) Each platform lift must comply with the requirements for private use lifts or public use lifts and with the requirements for all lifts.
(b) Each public use lift must
(1) Comply with the requirements for public use lifts and with the requirements for all lifts.
(2) Bear a label with the words “DOT - - Public Use Lift” as certification of compliance with the requirements specified in paragraph S6(b)(1).
(c) Each private use lift must
(1) Comply with the requirements for private use lifts and with the requirements for all lifts.
(2) Bear a label with the words “DOT - - Private Use Lift” as certification of compliance with the requirements specified in S6(c)(1).
(d) Platform lifts suitable for installation on buses, school buses, and MPVs other than motor homes with a GVWR greater than 4,536 kg (10,000 lb.), except motor homes, must be certified by the manufacturer as meeting the requirements for public use lifts. For platform lifts suitable for installation on all other vehicles, the manufacturer may select the option of certifying compliance with either the public use lift requirements or the private use lift requirements of this standard at the time it certifies the vehicle and may not thereafter select a different option for the vehicle.
(e) For all lifts, where a range of values is specified, the equipment must meet the requirements at all points within the range.
(f) The test procedures in S7 are used to determine compliance with all requirements, except S6.6, S6.7.5, S6.12 and S6.13.
S6.1 Threshold warning signal.
S6.1.1 Except when the platform lift is operated manually in backup mode as required by S6.9, the lift must meet the requirements of S6.1.2 and S6.1.3. The lift is tested in accordance with S7.4 to determine compliance with this section.
S6.1.2. Private-use lifts: Except for platform lifts where platform loading takes place wholly over the vehicle floor, a visual or audible warning must activate if the platform is more than 25 mm (1 inch) below the platform threshold area and portions of a passenger's body or mobility aid is on the platform threshold area defined in S4 when tested in accordance with S7.4.
S6.1.3 Public-use lifts: A visual and audible warning must activate if the platform is more than 25 mm (1 inch) below the platform threshold area and portions of a passenger's body or mobility aid is on the platform threshold area defined in S4 when tested in accordance with S7.4.
S6.1.4 The visual warning required by S6.1.2 and S6.1.3 must be a flashing red beacon as defined in SAE Recommended Practice J578 (1995) (incorporated by reference, see § 571.5), must have a minimum intensity of 20 candela, a frequency from 1 to 2 Hz, and must be located within the interior of the vehicle such that it is visible from a point 914 mm (3 ft) above the center of the threshold area (see Figure 2) wherever the lift is installed and with any configuration of the vehicle interior.
S6.1.5 The audible warning required by S6.1.2 and S6.1.3 must be a minimum of 85 dBA between 500 and 3000 Hz.
S6.1.6 The intensity of the audible warning and visibility of the visual warning required by S6.1.2 and S6.1.3 is measured/observed at a location 914 mm (3 ft) above the center of the platform threshold area. (See Figure 2).
S6.2 Platform lift operational requirements.
S6.2.1 General. Throughout the range of passenger operation and during the lift operations specified in S7.9.3 through S7.9.8, the platform lift must meet the requirements of S6.2.2 through S6.2.4. These requirements must be satisfied both with and without a standard load on the lift platform, except for S6.2.2.2, which must be satisfied without any load.
S6.2.2 Maximum platform velocity.
S6.2.2.1 Throughout the range of passenger operation specified in S7.9.4 through S7.9.7, both the vertical and horizontal velocity of the platform must be less than or equal to 152 mm (6 inches) per second when measured at the geometric center of the platform when the platform is unloaded and at the geometric center of the top, horizontal surface of the standard load specified in S7.1.1 when the platform is loaded.
S6.2.2.2 Except for platform lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold), during the stow and deploy operations specified in S7.9.3 through S7.9.8, both the vertical and horizontal velocity of any portion of the platform must be less than or equal to 305 mm (12 inches) per second.
S6.2.3 Maximum platform acceleration. Throughout the range of passenger operation specified in S7.9.4 through S7.9.7, both the horizontal and vertical acceleration of the platform must be less than or equal to 0.3 g after the accelerometer output is filtered with a channel frequency class (CFC) 3 filter. The filter must meet the requirements of SAE Recommended Practice J211/1 MAR95 (incorporated by reference, see § 571.5), with FH = 3 Hz and FN = 5 Hz. The accelerometer is located at the geometric center of the platform and is mounted directly on the platform when it is unloaded and on the geometric center of the top, horizontal surface of the standard load specified in S7.1.1 when the platform is loaded.
S6.2.4 Maximum noise level of public use lifts. Except as provided in S6.1.5, throughout the range of passenger operation specified in S7.9.4 through S7.9.7, the noise level of a public use lift may not exceed 80 dBa as measured at any lift operator's position designated by the platform lift manufacturer for the intended vehicle and in the area on the lift defined in S6.4.2.1. Lift operator position measurements are taken at the vertical centerline of the control panel 30.5 cm (12 in) out from the face of the control panel. In the case of a lift with a pendant control (i.e., a control tethered to the vehicle by connective wiring), measurement is taken at the vertical centerline of the control panel 30.5 cm (12 in) out from the face of the control panel while the control panel is in its stowed or stored position. For the lift operator positions outside of the vehicle, measurements are taken at the intersection of a horizontal plane 157 cm (62 in) above the ground and the vertical centerline of the face of the control panel after it has been extended 30.5 cm (12 in) out from the face of the control panel.
S6.3 Environmental resistance.
S6.3.1 Internally mounted platform lifts. On platform lifts and their components internal to the occupant compartment of the vehicle or internal to other compartments that provide protection from the elements when stowed, attachment hardware must be free of ferrous corrosion on significant surfaces except for permissible ferrous corrosion, as defined in § 571.209, at peripheral surface edges or edges of holes on under-floor reinforcing plates and washers after being subjected to the conditions specified in S7.3. Alternatively, such hardware must be made from corrosion-resistant steel containing at least 11.5 percent chromium per § 571.209, S5.2(a) or must be protected against corrosion by an electrodeposited coating of nickel, or copper and nickel with at least a service condition number of SC2, and other attachment hardware must be protected by an electrodeposited coating of nickel, or copper and nickel with a service condition number of SC1, in accordance with ASTM B456-95 (incorporated by reference, see § 571.5), but such hardware may not be racked for electroplating in locations subjected to maximum stress. The manufacturer shall select the option by the time it certifies the lift and may not thereafter select a different option for the lift. The lift must be accompanied by all attachment hardware necessary for its installation on a vehicle.
S6.3.2 Externally mounted platform lifts. On platform lifts and their components external to the occupant compartment of the vehicle and external to other compartments that provide protection from the elements when stowed, the lift and its components must be free of ferrous corrosion on significant surfaces except for permissible ferrous corrosion, as defined in FMVSS No. 209, at peripheral surface edges and edges of holes and continue to function properly after being subjected to the conditions specified in S7.3. Alternatively, such lifts and all associated hardware and components must be completely made from corrosion-resistant steel containing at least 11.5 percent chromium per FMVSS 571.209, S5.2(a). The manufacturer shall select the option by the time it certifies the lift and may not thereafter select a different option for the lift. The lift must be accompanied by all attachment hardware necessary for its installation on a vehicle.
S6.4 Platform requirements.
S6.4.1 General. Throughout the range of passenger operations and during the platform lift operations specified in S7.9.4 through S7.9.7, the platform lift must meet the requirements of S6.4.2 through S6.4.12. The requirements of S6.4.2 through S6.4.6, S6.4.7.4, S6.4.9.4, S6.4.9.5, S6.4.9.6, and S6.4.9.8 must be satisfied both with and without a standard load on the lift platform
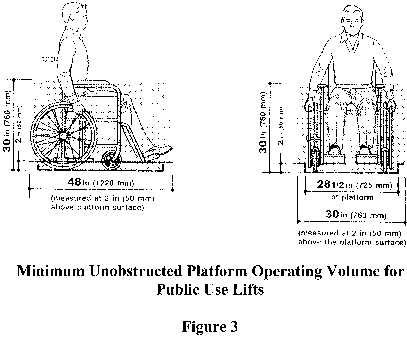
S6.4.2 Unobstructed platform operating volume.
S6.4.2.1 Public use lifts. For public use lifts, the minimum platform operating volume is the sum of an upper part and a lower part (see Figure 3). The lower part is a rectangular solid whose base is 725 mm (28.5 in) wide by the length of the platform surface, whose height is 50 mm (2 in), and which is resting on the platform surface with each side of the base parallel with the nearest side of the platform surface. The width is perpendicular to the lift reference plane and the length is parallel to the lift reference plane (See Figure 1). The upper part is a rectangular solid whose base is 760 mm (30 in) by 1,220 mm (48 in) long, whose height is 711 mm (28 in), and whose base is tangent to the top surface of the lower rectangular solid (see Figure 3). The centroids of both the upper and lower parts coincide with the vertical centroidal axis of the platform reference plane (see Figure 1).
S6.4.2.2 Private use lifts. For private use lifts, the platform operating volume is as specified by the lift manufacturer and identified in the lift insert to the vehicle owner's manual.
S6.4.3 Platform surface protrusions.
S6.4.3.1 Public use lifts. For public use lifts, except as required for deployment of the wheelchair retention device and inner roll stop, throughout the range of passenger operation, the platform surface may not have protrusions which rise more than 6.5 mm (0.25 in) above the platform surface, measured perpendicular to the platform surface by a device with its base centered between 50-100 mm (2-4 in) from the protrusion. Any cross-sectional dimension of the base of the protrusion measurement device must be greater than or equal to 25mm (1 in) and less than or equal to 50 mm (2 in).
S6.4.3.2 Private use lifts. For private use lifts, except as required for deployment of the wheelchair retention device and inner roll stop, the platform surface may not have protrusions which rise more than 13 mm (0.5 in) above the platform surface, measured perpendicular to the platform surface by a device with its base centered between 50-100 mm (2-4 in) from the protrusion. All portions of the sides of a protrusion that are between 6.5 mm (0.25 in) and 13 mm (0.5 in) above the platform must have a slope not greater than 1:2, measured with respect to the platform surface at the location of the protrusion. Any cross-sectional dimension of the base of the protrusion measurement device must be greater than or equal to 25mm (1 in) and less than or equal to 50 mm (2 in).
S6.4.4 Gaps, transitions and openings.
S6.4.4.1 When the platform lift is at the ground level loading position, any vertical surface transition measured perpendicular to the ground over which a passenger may traverse to enter or exit the platform, may not be greater than 6.5 mm (0.25 in). When the lift is at the vehicle level loading position, any vertical surface transition measured perpendicular to the platform threshold area over which a passenger may traverse to enter or exit the platform, may not be greater than 6.5 mm (0.25 in).
S6.4.4.2 When the platform lift is at the ground or vehicle level loading position, the slope of any surface over which a passenger may traverse to enter or exit the platform must have a rise to run not greater than 1:2 on the portion of the rise between 6.5 mm (0.25 in) and 13 mm (0.5 in), and 1:8 on the portion of the rise between 13 mm (0.5 in) and 75 mm (3 in). The rise of any sloped surface may not be greater than 75 mm (3 inches). When the lift is at the ground level loading position, measurements are made perpendicular to the ground. When the lift is at the vehicle level loading position, measurements are made perpendicular to the platform threshold area.
S6.4.4.3 When the inner roll stop or any outer barrier is deployed, any gap between the inner roll stop and lift platform and any gap between the outer barrier and lift platform must prevent passage of the clearance test block specified in S7.1.3 when its long axis is held perpendicular to the platform reference plane.
S6.4.4.4 When the platform is at the vehicle floor or ground level loading position, any horizontal gap over which a passenger may traverse to enter or exit the platform must prevent passage of a 13 mm (0.5 inch) diameter sphere.
S6.4.4.5 Any opening in that portion of the platform surface that coincides with the unobstructed platform operating volume described in S6.4.2 must prevent passage of a 19 mm (0.75 inch) diameter sphere.
S6.4.4.6 Any gap between the platform sides and edge guards which move with the platform must prevent passage of a 13 mm (0.5 inch) diameter sphere. Where structures fixed to the vehicle are used as edge guards, the horizontal gap between the platform side and vehicle structure must prevent passage of a 6.5 mm (0.25 inch) diameter sphere.
S6.4.5 Platform deflection. The angle of the deployed platform, when stationary, and loaded with a standard load, must not exceed 4.8 degrees with respect to the vehicle floor and must not exceed 3 degrees with respect to the platform's unloaded position. The angles are measured between a vertical axis from the vehicle floor and an axis normal to the platform center as shown in Figure 1.
S6.4.6 Edge guards.
S6.4.6.1 The platform lift must have edge guards that extend continuously along each side of the lift platform to within 75 mm (3 inches) of the edges of the platform that are traversed while entering and exiting the platform at both the ground and vehicle floor level loading positions. The edge guards must be parallel to the direction of wheelchair movement during loading and unloading. Alternatively, when tested in accordance with S7.7.4, all portions of the wheels of the wheelchair test device must remain above the platform surface and after the control is released to Neutral, at the end of each attempt to steer the test device off the platform, all wheels of the wheelchair test device must be in contact with the platform surface. The manufacturer shall select the option by the time it certifies the lift and may not thereafter select a different option for the lift.
S6.4.6.2 Edge guards that move with the platform must have vertical sides facing the platform surface and a minimum height of 38 mm (1.5 inches), measured vertically from the platform surface.
S6.4.6.3 Except whenever any part of the platform surface is below a horizontal plane 75 mm (3 inches) above the ground, edge guards must be deployed throughout the range of passenger operation.
S6.4.7 Wheelchair retention.
S6.4.7.1 Impact
I. Except for platform lifts designed so that platform loading takes place wholly over the vehicle floor, the lift must have a means of retaining the test device specified in S7.1.2. After impact, the test device must remain supported by the platform surface with none of the axles of its wheels extending beyond a plane that is perpendicular to the platform reference plane (Figure 1) and that is tangent to the edge of the platform that is traversed when entering or exiting the platform from the ground level loading position throughout its range of passenger operation, except as provided in S6.4.7.4. The lift is tested in accordance with S7.7 to determine compliance with this section.
S6.4.7.2 Impact II. For platform lifts designed so that platform loading takes place wholly over the vehicle floor, the lift must have a means of retaining the test device specified in S7.1.2. After impact, the test device must remain upright with all of its wheels on the platform surface, throughout the range of passenger operation, except as provided in S6.4.7.4. The lift is tested in accordance with S7.7 to determine compliance with this section.
S6.4.7.3 Overload. The deployed wheelchair retention device(s) must be capable of sustaining 7,117 N (1,600 lb force) when tested in accordance with S7.13. No separation, fracture, or breakage of the wheelchair retention device may occur as a result of conducting the test in S7.13.
S6.4.7.4 Deployment. Except whenever any part of the platform surface is below a horizontal plane 75 mm (3 in) above the ground, the wheelchair retention device(s) must be deployed throughout the range of passenger operation.
S6.4.8 Inner roll stop.
S6.4.8.1 Public use lifts. Public use lifts must have an inner roll stop that meets the requirements of S6.4.8.3.
S6.4.8.2 Private use lifts. Private use lifts must:
(a) Have an inner roll stop that meets the requirements of S6.4.8.3; or
(b) Have operating instructions near the lift controls and in the vehicle owner's manual, as specified in S6.7.8 and S6.12.4.3, that contain a warning that wheelchairs should back onto the platform when entering from the ground.
S6.4.8.3 Requirements. When tested in accordance with S7.8, platform lifts must have an inner roll stop that provides a means that prevents:
(a) The front wheels of the test device specified in S7.1.2 from extending beyond a plane that is perpendicular to the platform reference plane (Figure 1) and that is tangent to the edge of the platform where the roll stop is located when the lift is at ground level loading position; and
(b) Any portion of the test device specified in S7.1.2 from being contacted simultaneously with a portion of the lift platform and any other structure, throughout the lift's range of passenger operation.
S6.4.9 Handrails.
S6.4.9.1 Public use lifts: Public use lifts must have a handrail located on each side of the lift that meets the requirements of S6.4.9.3 through S6.4.9.9.
S6.4.9.2 Private use lifts: Private use lifts are not required to be equipped with handrails. Private use lifts that are equipped with handrails must meet the requirement of S6.4.9.3 through S6.4.9.9.
S6.4.9.3 The graspable portion of each handrail may not be less than 760 mm (30 inches) and more than 965 mm (38 inches) above the platform surface, measured vertically.
S6.4.9.4 The cross section of the graspable portion of each handrail may not be less than 31.5 mm (1.25 inches) and more than 38 mm (1.5 inches) in diameter or width, and may not have less than a 3.2 mm (0.125 inch) radii on any corner.
S6.4.9.5 The vertical projection of the graspable portion of each handrail must intersect two planes that are perpendicular to the platform reference plane and to the direction of travel of a wheelchair on the lift when entering or exiting the platform, and are 203 mm (8 inches) apart.
S6.4.9.6 The handrails must move such that the position of the handrails relative to the platform surface does not change.
S6.4.9.7 When tested in accordance with S7.12.1, each handrail must withstand 445 N (100 pounds force) applied at any point and in any direction on the handrail without more than 25 mm (1 inch) of displacement relative to the platform surface. After removal of the load, the handrail must exhibit no permanent deformation.
S6.4.9.8 When tested in accordance with S7.12.1, there must be at least 38 mm (1.5 inches) of clearance between each handrail and any portion of the vehicle, throughout the range of passenger operation.
S6.4.9.9 When tested in accordance with S7.12.2, each handrail must withstand 1,112 N (250 lb/f) applied at any point and in any direction on the handrail without sustaining any failure, such as cracking, separation, fracture, or more than 100 mm (4 inches) of displacement of any point on the handrails relative to the platform surface.
S6.4.10 Platform markings on public use lifts. Throughout the range of passenger operation, all edges of the platform surface, the visible edge of the vehicle floor or bridging device adjacent to the platform lift, and any designated standing area on a public use lift must be outlined. The outlines must be at least 25 mm (1 in) wide and of a color that contrasts with its background by 60 percent, determined according to the following equation:
Contrast = 100 × [(L1−L2)/L1]
Where:
L1 = luminance of the lighter color or shade, and
L2 = luminance of the darker color or shade.
L1 and L2 are measured perpendicular to the platform surface with illumination provided by a diffuse light and a resulting luminance of the platform surface of 323 lm/m2 (30 lumen/sqft).
S6.4.11 Platform slip resistance. When tested in accordance with S7.2, the coefficient of friction, in any direction, of any part of a wet platform surface may not be less than 0.65.
S6.5 Structural integrity.
S6.5.1 Fatigue endurance.
S6.5.1.1 Public use lifts. Except for lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold), public use lifts must remain operable when operated through a total of 15,600 cycles: 7,800 unloaded Raise/Lower and Stow/Deploy operations and 7,800 loaded Raise/Lower operations as specified in S7.10. Public use lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold) must remain operable when operated through a total of 15,600 cycles: 7,800 unloaded Raise/Lower operations and 7,800 loaded Raise/Lower operations. No separation, fracture, or breakage of any vehicle or lift component may occur as a result of conducting the fatigue test in S7.10.
S6.5.1.2 Private use lifts. Except for lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold), private use lifts must remain operable when operated through a total of 4,400 cycles: 2,200 unloaded Raise/Lower and Stow/Deploy operations and 2,200 loaded Raise/Lower operations as specified in S7.10. Private use lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold) must remain operable when operated through a total of 4,400 cycles: 2,200 unloaded Raise/Lower operations and 2,200 loaded Raise/Lower operations. No separation, fracture, or breakage of any vehicle or lift component may occur as a result of conducting the fatigue test in S7.10.
S6.5.2 Proof load. The platform lift must be capable of holding three times the standard load, as specified in S7.11, without separation, fracture, or breakage of any vehicle or lift component. After the test, the lift must pass Static Load Test I as specified in S7.9.
S6.5.3 Ultimate load. The platform lift must be capable of holding four times the standard load, as specified in S7.14, without separation, fracture, or breakage of the platform, supporting structure, or lifting mechanism.
S6.6 Platform free fall limits. In the event of any single-point failure of systems for raising, lowering or supporting the platform, any portion of the platform, loaded as specified in S7.1.1, may not fall vertically faster than 305 mm (12 in) per second or change angular orientation more than 2 degrees from the orientation prior to the failure. This requirement applies whenever the lift is under primary power source operation or manual backup operation.
S6.7 Control panel switches.
S6.7.1 The platform lift must meet the requirements of S6.7.2 through S6.7.8 and, when operated by means of the control panel switches specified in S6.7.2, must perform the lift operations specified in S7.9.
S6.7.2 The platform lift system must have control panel switches that perform not less than the following functions: (platform lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold) are exempt from S6.7.2.2 and S6.7.2.5).
S6.7.2.1 Enables and disables the lift control panel switches. This function must be identified as “POWER” if located on the control. The POWER function must have two states: “ON” and “OFF”. The “ON” state must allow platform lift operation. When the POWER function is in the “ON” state, an indicator light on the controls must illuminate. The “OFF” state must prevent lift operation and must turn off the indicator light. Verification with this requirement is made throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.3 through S7.9.8.
S6.7.2.2 Moves the lift from a stowed position to an extended position or, to one of the two loading positions. This function must be identified as “DEPLOY” or “UNFOLD” on the control.
S6.7.2.3 Lowers the lift platform. This function must be identified as “Down” or “Lower” on the control.
S6.7.2.4 Raises the lift platform. This function must be identified as “Up” or “Raise” on the control.
S6.7.2.5 Moves the lift from a position within the range of passenger operation to a stowed position. This function must be identified as “Stow” or “Fold” on the control.
S6.7.3 Except for the Power function described in S6.7.2.1, the functions specified in S6.7.2 must activate in a momentary fashion, by one switch or by a combination of switches. Verification with this requirement is made throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.3 through S7.9.8.
S6.7.4 Except for the POWER function described in S6.7.2.1, the control system specified in S6.7.2 must prevent the simultaneous performance of more than one function. If an initial function is actuated, then one or more other functions are actuated while the initial function remains actuated, the platform must either continue in the direction dictated by the initial function or stop. Verification of this requirement is made throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.3 through S7.9.8.
S6.7.5 Any single-point failure in the control panel switches may not prevent the operation of any of the interlocks as specified in S6.10.
S6.7.6 Identification of operating functions.
S6.7.6.1 Each operating function of each platform lift control must be identified with characters that are at least 2.5 mm (0.1 in) in height.
S6.7.6.2 Public use lifts. Public-use lift controls located within the portion of the passenger compartment specified in S5.3.4(a) of Standard No. 101 (§ 571.101) must have characters that are illuminated in accordance with S5.3 of Standard No. 101 when the vehicle's headlights are illuminated. Public-use lift controls located outside the portion of the passenger compartment specified in S5.3.4(a) of Standard No. 101 (§ 571.101) must have means for illuminating the characters to make them visible under daylight and nighttime conditions.
S6.7.7 Control location for public use lifts: In public use lifts, except for the backup operation specified in S6.9, all control panel switches must be positioned together and in a location such that the lift operator has a direct, unobstructed view of the platform lift passenger and the passenger's mobility aid, if applicable. Verification with this requirement is made throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.3 through S7.9.8. Additional controls may be positioned in other locations.
S6.7.8 Operating instructions: Simple instructions regarding the platform lift operating procedures, including backup operations as specified by S6.9, must:
S6.7.8.1 Be located near the controls.
S6.7.8.2 Have characters with a minimum height of 2.5 mm (0.1 in) and written in English.
S6.7.8.3 Public use lifts: Include the statement “DOT - Public Use Lift”.
S6.7.8.4 Private use lifts: Include the statement “DOT - Private Use Lift”, the manufacturer's rated load for the lift, and, if applicable, instructions indicating that the wheelchair occupant must back onto the lift when loading from the ground.
S6.8 Jacking prevention.
S6.8.1 Except when the platform lift is operated in backup mode as required by S6.9, throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.4 and S7.9.7, the lift system must meet the requirements of S6.8.2, both with and without a standard load on the lift.
S6.8.2 The control system or platform lift design must prevent the raising of any portion of the vehicle by the lift system when lowering the lift is attempted while the lift is at the ground level loading position.
S6.9 Backup operation.
S6.9.1 The platform lift must be equipped with a manual backup operating mode that can, in the event there is a loss of the primary power source for lift operation or a lift malfunction, deploy the lift, lower the loaded platform to the ground level loading position, raise the unloaded platform to the vehicle floor loading position, and stow the lift. During backup operation of the lift, the wheelchair retention device and inner roll stop must be manually deployable and stowable. The operating instructions near the lift controls and in the vehicle owner's manual insert, as specified in S6.7.8 and S6.12.2, must contain information on manual backup operation which must include manual operation of the wheelchair retention device and inner roll stop during backup operation of the lift.
S6.10 Interlocks.
S6.10.1 Except when the platform lift is operated in backup mode as required by S6.9, the requirements of S6.10.2 must be met, both with and without a standard load on the lift.
S6.10.2 The platform lift system must have interlocks or operate in such a manner when installed according to the installation instructions, as to prevent:
S6.10.2.1 Forward or rearward mobility of the vehicle unless the platform lift is stowed. The design of this system must be such that it discourages accidental release and does not affect vehicle movement when the lift is stowed until the vehicle is stopped and the lift deployed. Verification with this requirement is made throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.2 and S7.9.3.
S6.10.2.2 Operation of the platform lift from the stowed position until forward and rearward mobility of the vehicle is inhibited, by means of placing the transmission in park or placing the transmission in neutral and actuating the parking brake or the vehicle service brakes by means other than the operator depressing the vehicle's service brake pedal. Verification with this requirement is made throughout the lift operations specified in S7.9.2 and S7.9.3.
S6.10.2.3 Stowing of the platform lift when occupied by portions of a passenger's body, and/or a mobility aid. Platform lifts designed to be occupied while stowed and platform lifts that manually stow (fold) are excluded from this requirement. Verification with this requirement is made using the test device specified in S7.1.4. Move the deployed platform lift to a position within the range of passenger operation where it will stow if the control specified in S6.7.2.5 is actuated. Place the test device specified in S7.1.4 on its narrowest side on any portion of the platform surface that coincides with the unobstructed platform operating volume described in S6.4.2. Using the operator control specified in S7.7.2.5, attempt to stow the lift. The interlock must prevent the lift from stowing.
S6.10.2.4 Movement of the platform up or down, throughout the range of passenger operation, unless the inner roll stop required to comply with S6.4.8 is deployed. When the platform reaches a level where the inner roll stop is designed to fully deploy, the platform must stop unless the inner roll stop has fully deployed. Verification with this requirement is made by performing the test procedure specified in S7.6.1.
S6.10.2.5 Movement of the platform up or down, throughout the range of passenger operation, when the highest point of the platform surface at the outer most platform edge is above a horizontal plane 75 mm (3 in) above the ground level loading position, unless the wheelchair retention device required to comply with S6.4.7 is deployed throughout the range of passenger operations. Verification of compliance is made using the test procedure specified in S7.5.1.
S6.10.2.6 In the case of a platform lift that is equipped with an outer barrier, vertical deployment of the outer barrier when it is occupied by portions of the passenger's body or mobility aid throughout the lift operation. When the platform stops, the vertical change in distance of the horizontal plane (passing through the point of contact between the wheelchair test device wheel(s) and the upper surface of the outer barrier) must not be greater than 13 mm (0.5 in). Verification of compliance with this requirement is made using the test procedure specified in S7.5.1.
S6.10.2.7 Vertical deployment of the inner roll stop required to comply with S6.4.8 when it is occupied by portions of a passenger's body or mobility aid throughout the lift operations. When the platform stops, the vertical change in distance of the horizontal plane (passing through the point of contact between the wheelchair test device wheel(s) and the upper surface of the inner roll stop or platform edge) must not be greater than 13 mm (0.5 in). Verification of compliance with this requirement is made using the test procedure specified in S7.6.1.
S6.11 Operations counter. The platform lift must have an operation or cycle counter that records each complete Up/Down (Raise/Lower) operation throughout the range of passenger operation. Determination of compliance with this requirement is made during the lift operations specified in S7.9.4 and S7.9.5.
S6.12 Vehicle owner's manual insert. The lift manufacturer must provide with the lift, inserts for the vehicle owner's manual that provide specific information about the platform lift. The vehicle owner's manual insert must be written in English and must include:
S6.12.1 A maintenance schedule that includes maintenance requirements that have, at a minimum, some dependency on the number of cycles on the operations counter specified in S6.11.
S6.12.2 Instructions regarding the platform lift operating procedures, including backup operations, as specified by S6.9.
S6.12.3 Public use lifts: In addition to meeting the requirements of S6.12.1 and S6.12.2, the owner's manual insert for public use lifts must also include:
S6.12.3.1 The statement “DOT - Public Use Lift” on the front cover of the vehicle owner's manual insert; and
S6.12.3.2 The statement “DOT - Public Use Lift” verifies that this platform lift meets the “public use lift ” requirements of FMVSS No. 403. This lift may be installed on all vehicles appropriate for the size and weight of the lift, but must be installed on buses, school buses, and multi-purpose passenger vehicles other than motor homes with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) that exceeds 4,536 kg (10,000 lb).”
S6.12.4 Private use lifts: In addition to meeting the requirements of S6.12.1 and S6.12.2, the owner's manual insert for private use lifts must also include:
S6.12.4.1 The dimensions that constitute the unobstructed platform operating volume;
S6.12.4.2 The manufacturer's rated load for the lift;
S6.12.4.3 Information on whether a wheelchair user must back onto the platform from the ground level loading position due to the absence of an inner roll stop;
S6.12.4.4 The statement “DOT-Private Use Lift” on the front cover of the vehicle owner's manual insert; and
S6.12.4.5 The statement “DOT-Private Use Lift verifies that this platform lift meets only the “private use lift” requirements of FMVSS No. 403. This lift may be installed on all vehicles appropriate for the size and weight of the lift, except for buses, school buses, and multi-purpose passenger vehicles other than motor homes with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) that exceeds (4,536 kg) 10,000 lb.”
S6.13 Installation instructions. The manufacturer of a platform lift must include installation instructions with each lift. Information must be included in the installation instructions that identifies:
S6.13.1 The vehicles on which the lift is designed to be installed. Vehicles may be identified by listing the make, model, and year of the vehicles for which the lift is suitable, or by specifying the design elements that would make a vehicle an appropriate host for the particular lift, and for which the platform lift manufacturer has certified compliance.
S6.13.2 Procedures for operational checks that the vehicle manufacturer must perform to verify that the lift is fully operational. Such checks include, but are not limited to, platform lighting, the threshold-warning signal, and interlocks, including those that interface with vehicle systems.
S6.13.3 Any informational material or labels that must be placed on or in the vehicle in order to comply with the requirements of this standard. Labels must be of a permanent nature that can withstand the elements of the outside environment.
S6.13.4 Public use lifts: In addition to meeting the requirements of S6.13.1 through S6.13.3, the installation instructions for public use lifts must also include, on the front cover of the instructions, the statement “DOT-Public Use Lift”.
S6.13.4.1 Installation instructions for public use lifts must contain the statement “Public use vehicle manufacturers are responsible for complying with the lift lighting requirements in Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard No. 404, Platform Lift Installations in Motor Vehicles (49 CFR 571.404).”
S6.13.5 Private use lifts: In addition to meeting the requirements of S6.13.1 through S6.13.3, the installation instructions for private use lifts must also include, on the front cover of the instructions, the manufacturer's rated load for the lift and the statement “DOT-Private Use Lift”.
S7 Test conditions and procedures. Each platform lift must be capable of meeting all of the tests specified in this standard, both separately, and in the sequence specified in this section. The tests specified in S7.4, S7.7.4 and S7.8 through S7.12 are performed on a single lift and vehicle combination. The tests specified in S7.2, S7.3, S7.5, S7.6, S7.7.1, S7.13, and S7.14 may be performed with the lift installed on a test jig rather than on a vehicle. Tests of requirements in S6.1 through S6.11 may be performed on a single lift and vehicle combination, except for the requirements of S6.5.3. Attachment hardware may be replaced if damaged by removal and reinstallation of the lift between a test jig and vehicle.
S7.1 Test devices.
S7.1.1 Test pallet and load. The surface of the test pallet that rests on the platform used for the tests specified in S7.9 through S7.11 and S7.14 has sides that measure between 660 mm (26 in) and 686 mm (27 in). For the tests specified in S7.9 and S7.10, the test pallet is made of a rectangular steel plate of uniform thickness and the load that rests on the test pallet is made of rectangular steel plate(s) of uniform thickness and sides that measure between 533 mm (21 in) and 686 mm (27 in). The standard test load that rests on the pallet is defined in S4.
S7.1.2 Wheelchair test device. The test device is an unloaded power wheelchair whose size is appropriate for a 95th percentile male and that has the dimensions, configuration and components described in S7.1.2.1 through S7.1.2.11. If the dimension in S7.1.2.9 is measured for a particular wheelchair by determining its tipping angle, the batteries are prevented from moving from their original position.
S7.1.2.1 a cross-braced steel frame;
S7.1.2.2 a sling seat integrated in the frame;
S7.1.2.3 a belt drive;
S7.1.2.4 detachable footrests, with the lowest point of the footrest adjustable in a range not less than 25 mm (1 in) to 123 mm (5 in) from the ground;
S7.1.2.5 Two pneumatic rear tires with a diameter not less than 495 mm (19.5 in) and not more than 521 mm (20.5 in) inflated to the wheelchair manufacturer's recommended pressure or if no recommendation exists, to the maximum pressure that appears on the sidewall of the tire;
S7.1.2.6 Two pneumatic front tires with a diameter not less than 190 mm (7.5 in) and not more than 216 mm (8.5 in) inflated to the wheelchair manufacturer's recommended pressure or if no recommendation exists, to the maximum pressure that appears on the sidewall of the tire;
S7.1.2.7 a distance between front and rear axles not less than 457 mm (18 in) and not more than 533 mm (21 in);
S7.1.2.8 a horizontal distance between rear axle and center of gravity not less than 114 mm (4.5 in) and not more than 152 mm (6.0 in);
S7.1.2.9 a vertical distance between ground and center of gravity not less than 260 mm (10.25 in) and not more than 298 mm (11.75 in);
S7.1.2.10 a mass of not less than 72.5 kg (160 lb) and not more than 86.0 kg (190 lb).
S7.1.2.11 Batteries with a charge not less than 75 percent of their rated nominal capacity (for tests that require use of the wheelchair's propulsion system).
S7.1.3 Clearance test block for gaps, transitions, and openings. The clearance test block is made of a rigid material and is 16 × 16 × 100 mm (0.625 × 0.625 × 4.0 in) with all corners having a 1.6 mm (0.0625 inch) radius.
S7.1.4 Test Device for detecting platform occupancy. Occupancy of the platform is detected using a 152 × 152 × 305 mm (6 × 6 × 12 inches) rigid box having a total weight of 22.7 kg (50 lb).
S7.2 Slip resistance test.
S7.2.1 To determine compliance with S6.4.12, clean any 450mm × 100mm (17.5 in × 3.94 in) section of the platform with household glass cleaner (ammonia hydroxide solution). Wet the cleaned section of the platform by evenly spraying 3 ml (0.10 oz) of distilled water per 100 cm2 (15.5 in2) of surface area. Begin the test specified in S7.2.2 within 30 seconds of completion of the wetting process.
S7.2.2 Use the test procedure defined in ANSI/RESNA Standard WC/Vol. 1-1998, Section 13 (incorporated by reference, see § 571.5), except for clauses 5.3, Force Gage and 6, Test Procedure, on the wet section of platform. In lieu of clauses 5.3 and 6, implement the requirements of S7.2.2.1 and S7.2.2.2.
S7.2.2.1 Force gage. The pulling force is measured, at a frequency of at least 10 Hz, by a force gauge that has been calibrated to an accuracy of ±2 percent of the reading in the range of 25N to 100N.
S7.2.2.2 Test procedure. Before the test, prepare the surface of the test rubber by lightly abrading with waterproof silicon carbide paper, grade P120, weight D (120 wet and dry). Then wipe the surface clean with a dry cloth or brush. No solvents or other cleaning materials are used. To determine the coefficient of friction for the wet platform section pull the test block, with the test rubber attached, by machine at a rate of 20 ±2mm/s. The machine and test block are rigidly linked by a device that exhibits a stiffness greater than or equal to 1 × 105 N/m. Pull the test block for a minimum of 13 seconds. Record the pulling force over the final 10 seconds of the test at a minimum frequency of 10 Hz. Repeat the test at least 5 times on any one area of the platform surface, in a single direction. Calculate the average pulling force for each trial, F1 through Fn, where n is the number of trials. Measure the weight of the test block with the force gauge and call it Fb. Calculate the coefficient of friction, μp, from the following equation:

S7.3 Environmental resistance test.
S7.3.1 Perform the procedures specified in S7.3.2 through S7.3.5 to determine compliance with S6.3.
S7.3.2 Attachment hardware, as specified in S6.3.1, and externally mounted platform lifts or components, as specified in S6.3.2, are tested in accordance with ASTM B117-97 (incorporated by reference, see § 571.5). Any surface coating or material not intended for permanent retention on the metal parts during service life are removed prior to testing. Except as specified in S7.3.3, the period of the test is 50 hours, consisting of two periods of 24 hours exposure to salt spray followed by one hour drying.
S7.3.3 For attachment hardware located within the occupant compartment of the motor vehicle or internal to other compartments that provide protection from the elements and not at or near the floor of the compartment, the period of the test is 25 hours, consisting of one period of 24 hours exposure to salt spray followed by one hour drying.
S7.3.4 For performance of this test, externally mounted platform lifts or components may be installed on test jigs rather than on the vehicle. The lift is in a stowed position. The configuration of the test setup is such that areas of the lift that would be exposed to the outside environment during actual use are not protected from the salt spray by the test jig.
S7.3.5 At the end of the test, any surface exposed to the salt spray is washed thoroughly with water to remove the salt. After drying for at least 24 hours under laboratory conditions, the platform lift and components are examined for ferrous corrosion on significant surfaces, i.e., all surfaces that can be contacted by a sphere 2 cm (0.79 in) in diameter.
S7.4 Threshold warning signal test.
S7.4.1 Determine compliance with S6.1.2 and S6.1.3 using the test procedure specified in S7.4.2.
S7.4.2 During the threshold warning test, the wheelchair test device may be occupied by a human representative of a 5th percentile female meeting the requirements of FMVSS 208, S29.1(f) and S29.2. If present, the human subject is seated in the wheelchair test device with his or her feet supported by the wheelchair foot rests which are adjusted properly for length and in the down position (not elevated). The manufacturer shall select the option by the time it certifies the lift and may not thereafter select a different test option for the lift. Maneuver the lift platform to the vehicle floor level loading position. Using the wheelchair test device specified in S7.1.2, place one front wheel of the wheelchair test device on any portion of the threshold area defined in S4. Move the platform down until the alarm is actuated. Remove the test wheelchair wheel from the threshold area to deactivate the alarm. Measure the vertical distance between the platform and the threshold area and determine whether that distance is greater than 25 mm (1 in).
S7.5 Outer barrier non-deployment interlock and occupied outer barrier interlock test.
S7.5.1 Determine compliance with both S6.10.2.5 and S6.10.2.6 by using the following single test procedure.
S7.5.1.1 Place the test jig or vehicle on which the lift is installed on a flat, level, horizontal surface. Maneuver the platform to the ground level loading position. Using the lift control, move the lift upward until the point where the outer barrier fully deploys. Stop the platform at that point and measure the vertical distance between the highest point on the platform surface at the outer most edge and the ground to determine whether the distance is greater than 75 mm (3 in). Reposition the platform in the ground level loading position. Locate the wheelchair test device specified in S7.1.2 on the platform. If other wheelchair retention devices (e.g., a belt retention device) prevent the front wheel of the wheelchair test device from accessing the outer barrier when on the platform, the wheelchair test device may be placed on the ground facing the entrance to the lift, with other retention devices configured so that they do not prevent lift operation (e.g., with any belt retention device fastened or buckled).
S7.5.1.2 Place one front wheel of the wheelchair test device on any portion of the outer barrier. If the platform is too small to maneuver one front wheel on the outer barrier, two front wheels may be placed on the outer barrier. Note the distance between a horizontal plane (passing through the point of contact between the wheelchair test device wheel(s) and the upper surface of the outer barrier) and the ground. Using the lift control, move the platform up until it stops. Measure the vertical distance between the highest point of the platform surface at the outer most edge and the ground to determine compliance with S6.10.2.5. Measure the vertical change in distance of the horizontal plane (passing through the point of contact between the wheelchair test device wheel(s) and the upper surface of the outer barrier) to determine compliance with S6.10.2.6.
S7.6 Inner roll stop non-deployment interlock and occupied inner roll stop interlock test.
S7.6.1 Determine compliance with both S6.10.2.4 and S6.10.2.7 by using the single test procedure in S7.6.2 and S7.6.3.
S7.6.2 Maneuver the platform to the vehicle floor level loading position, and position the wheelchair test device specified in S7.1.2 on the platform with the front of the wheelchair test device facing the vehicle. Using the lift control, move the platform down until the inner roll stop fully deploys. Stop the lift and note that location.
S7.6.3 Reposition the platform at the vehicle floor level loading position. Place one front wheel of the wheelchair test device on the inner roll stop. If the platform is too small to maneuver one front wheel on the inner roll stop, two front wheels may be placed on the inner roll stop. Note the vertical distance between a horizontal plane (passing through the point of contact between the wheelchair test device wheel(s) and the upper surface of the inner roll stop) and the ground. Using the lift control, move the platform down until it stops. Compare the location of the platform relative to the location noted in S7.6.2 to determine compliance with S6.10.2.4. Measure the vertical change in distance of the horizontal plane (passing through the point of contact between the wheelchair test device wheel(s) and the upper surface of the inner roll stop) to determine compliance with S6.10.2.7.
S7.7 Wheelchair retention device impact test and edge guard test.
S7.7.1 Determine compliance with S6.4.7.1 and S6.4.7.2 using the test device specified in S7.1.2, under the procedures specified in S7.7.2 and S7.7.3.
S7.7.2 Conduct the test in accordance with the procedures in S7.7.2.1 through S7.7.2.5 to determine compliance with S6.4.7.1. In the case of private use lifts, perform both S7.7.2.5(a) and (b), unless the operating directions specify a required direction of wheelchair movement onto the platform. When a direction is indicated in the operating instructions, perform the procedure specified in S7.7.2.5(a) or (b) with the test device oriented as required by the operating instructions.
S7.7.2.1 Place the lift platform at the vehicle floor loading position.
S7.7.2.2 If the wheelchair retention device is an outer barrier, the footrests are adjusted such that at their lowest point they have a height 25 mm ±2 mm (1 in ±0.08 in) less than the outer barrier. If the wheelchair retention device is not an outer barrier, the footrests are adjusted such that at their lowest point they have a height 50 mm ±2 mm (2 in ±0.08 in) above the platform.
S7.7.2.3 Position the test device with its plane of symmetry coincident with the lift reference plane and at a distance from the platform sufficient to achieve the impact velocities required by S7.7.2.5.
S7.7.2.4 An optional 50 kg (110 pounds) of weight may be centered, evenly distributed, and secured in the seat of the wheelchair test device to assist in stabilizing the wheelchair test device during testing. The manufacturer shall select the option by the time it certifies the lift and may not thereafter select a different test option for the lift. Accelerate the test device onto the platform under its own power such that the test device impacts the wheelchair retention device at each speed and direction combination specified in S7.7.2.5. Terminate power to the wheelchair test device by means of the wheelchair controller after completion of the initial impact of any portion of the wheelchair test device with the wheelchair retention device. Note the position of the wheelchair test device following each impact to determine compliance with S6.4.7. If necessary, after each impact, adjust or replace the footrests to restore them to their original condition.
S7.7.2.5 The test device is operated at the following speeds, in the following directions -
(a) At a speed of not less than 2.0 m/s (4.4 mph) and not more than 2.1 m/s (4.7 mph) in the forward direction.
(b) At a speed of not less than 1.75 m/s (3.9 mph) and not more than 1.85 m/s (4.1 mph) in the rearward direction.
S7.7.3 Rotary platform lifts: For rotary platform lifts, conduct the test under the procedures in S7.7.3.3 through S7.7.3.7 to determine compliance with S6.4.7.2.
S7.7.3.1 Public use lifts: For public use lifts, perform the test in both possible test device orientations.
S7.7.3.2 Private use lifts: For private use lifts, perform the test in both possible test device orientations unless a required direction of wheelchair movement onto the platform is indicated in the operating instructions. If a required direction is indicated in the operating instructions, perform the test with the test device oriented as required by the operating instructions.
S7.7.3.3 Adjust the footrests of the test device to the shortest length. Place the test device on the platform with its plane of symmetry coincident with the lift reference plane.
S7.7.3.4 Position the platform surface 90 mm ±10 mm (3.5 inches ±0.4 inches) above the ground level position.
S7.7.3.5 Slowly move the test device in the forward direction until it contacts a wheelchair retention device. Activate the controller of the test device such that, if the test device were unloaded and unrestrained on a flat, level surface, it would achieve a maximum forward velocity of not less than 2.0 m/s (4.4 mph) and not more than 2.1 m/s (4.7 mph).
S7.7.3.6 Realign the test device on the platform so that its plane of symmetry is coincident with the lift reference plane. Slowly move the test device in the rearward direction until it contacts a wheelchair retention device. Activate the controller of the test device such that, if the test device were unloaded and unrestrained on a flat, level surface, it would achieve a maximum rearward velocity of not less than 1.75 m/s (3.9 mph) and not more than 1.85 m/s (4.1 mph).
S7.7.3.7 During the impacts specified in S7.7.3.5 and S7.7.3.6, maintain power to the drive motors until all test device motion has ceased except rotation of the drive wheels. Note the position of the test device after its motion has ceased following each impact to determine compliance with S6.4.7.2.
S7.7.4 Edge Guard Test. Determine compliance with S6.4.6 using the test device specified in S7.1.2 by performing the test procedure specified in S7.7.4.1 through S7.7.4.6. During the edge guard tests, remove the footrests from the wheelchair test device.
S7.7.4.1 Position the platform surface 90 mm ±10 mm (3.5 in ±0.4 in) above the ground level loading position.
S7.7.4.2 Place the test device on the platform surface with its plane of symmetry coincident with the lift reference plane within ±10 mm (±0.4 in), its forward direction of travel inboard toward the vehicle, and its position on the platform as far rearward as the wheelchair retention device or outer barrier will allow it to be placed.
S7.7.4.3 Adjust the control of the test device to a setting that provides maximum acceleration and steer the test device from side-to-side and corner-to-corner of the lift platform, attempting to steer the test device off the platform. After each attempt, when the wheelchair test device stalls due to contact with a barrier, release the control to Neutral and realign the test device to the starting position. Repeat this sequence at any level that is more than 90 mm ±10 mm (3.5 in ±0.4 in) above the ground level loading position and more than 38 mm ±10 mm (1.5 in ±0.4 in) below the vehicle floor level loading position. Repeat this sequence at 38 mm ±10 mm (1.5 in ±0.4 in) below the vehicle floor level loading position.
S7.7.4.4 Next position the platform surface 38 mm ±10 mm (1.5 in ±0.4 in) below the vehicle floor level loading position.
S7.7.4.5 Reposition the test device on the platform surface with its plane of symmetry coincident with the lift reference plane within ±10 mm (±0.4 in), its forward direction of travel outboard away from the vehicle, and its position on the platform as far rearward as the wheelchair inner roll-stop or vehicle body will allow it to be placed.
S7.7.4.6 Adjust the control of the test device to a setting that provides maximum acceleration and steer the test device from side-to-side and corner-to-corner of the lift platform, attempting to steer the test device off the platform. After each attempt, when the wheelchair test device stalls due to contact with a barrier, release the control to Neutral and realign the test device to the starting position. Repeat this sequence at any level that is more than 90 mm ±10 mm (3.5 in ±0.4 in) above the ground level loading position and more than 38 mm ±10 mm (1.5 in ±0.4 in) below the vehicle floor loading position. Repeat this sequence at 38 mm ±10 mm (1.5 in ±0.4 in) below the vehicle floor level loading position.
S7.8 Inner roll stop test. Determine compliance with S6.4.8 using the test device specified in S7.1.2 in accordance with the procedures specified in S7.8.1 through S7.8.6.
S7.8.1 Place the platform at the ground level loading position, such that the platform is level.
S7.8.2 Adjust the footrests of the test device to the shortest length. Position the test device on the ground at a distance from the platform sufficient to achieve the impact velocity required by S7.8.3. The plane of symmetry of the test device is coincident with the lift reference plane and the forward direction of travel is onto the platform.
S7.8.3 An optional 50 kg (110 pounds) of weight may be centered, evenly distributed, and secured in the seat of the wheelchair test device to assist in stabilizing the wheelchair test device during testing. The manufacturer shall select the option by the time it certifies the lift and may not thereafter select a different test option for the lift. Accelerate the test device onto the platform such that it impacts the inner roll stop at a speed of not less than 1.5 m/s (3.4 mph) and not more than 1.6 m/s (3.6 mph). Terminate power to the wheelchair test device by means of the wheelchair controller after completion of the initial impact of any portion of the wheelchair test device with the inner roll stop. Determine compliance with S6.4.8.3(a).
S7.8.4 If necessary, adjust or replace the footrests to restore them to the condition they were in prior to the impact. Reposition the test device on the platform with its plane of symmetry coincident with the lift reference plane. Slowly move the test device in the forward direction until it contacts the inner roll stop.
S7.8.5 Apply a static load to the inner roll stop by activating the controller of the test device such that, with the test device were unrestrained on a flat and level surface, it achieves a maximum forward velocity of not less than 2.0 m/s and not more than 2.1 m/s.
S7.8.6 Maintain control activation and raise the platform to the vehicle loading position. Determine compliance with S6.4.8.3(b).
S7.9 Static load test I - working load.
S7.9.1 By use of the lift controls specified in S6.7.2, perform the operations specified in S7.9.2 through S7.9.8 in the order they are specified.
S7.9.2 Place the platform in the stowed position.
S7.9.3 Deploy the platform to the vehicle floor loading position. Center a standard load, including the test pallet, on the platform surface.
S7.9.4 Lower the lift platform from the vehicle floor loading position to the ground level loading position, stopping once between the two positions. Remove the test pallet from the lift platform.
S7.9.5 Raise the lift platform from the ground level loading position to the vehicle floor level loading position, stopping once between the two positions.
S7.9.6 Lower the lift platform from the vehicle floor level loading position to the ground level loading position, stopping once between the two positions.
S7.9.7 Center the loaded test pallet on the platform surface. Raise the lift platform from the ground level loading position to the vehicle floor loading position, stopping once between the two positions.
S7.9.8 Remove the pallet from the lift platform. Stow the lift.
S7.9.9 Turn power off to the lift and repeat S7.9.3 through S7.9.5 and stow the lift using the backup operating mode as specified by S6.9 in accordance with the manufacturer's backup operating instructions.
S7.10 Fatigue endurance test.
S7.10.1 Perform the test procedure specified in S7.10.2 through S7.10.6 and determine compliance with S6.5.1.
S7.10.2 Put the unloaded lift platform at the ground level loading position. Center a standard load, including the test pallet, on the platform surface.
S7.10.3 Each sequence of lift operations specified in S7.10.5.1, S7.10.5.2, S7.10.6.1 and S7.10.6.2 are done in blocks of 10 cycles with a 1 minute maximum rest period between each cycle in any block. The minimum rest period between each block of 10 cycles is such that the temperature of the lift components is maintained below the values specified by the manufacturer or that degrade the lift function.
S7.10.4 During the test sequence specified in S7.10.2 through S7.10.6, perform any lift maintenance as specified in the vehicle owner's manual.
S7.10.5 Public use lifts: Using the lift controls specified in S6.7.2, perform the operations specified in S7.10.5.1 through S7.10.5.3 in the order they are given. Public use lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold) are not required to perform the stow and deploy portions of the tests.
S7.10.5.1 Raise and lower the platform through the range of passenger operation 3,900 times.
S7.10.5.2 Remove the test pallet from the platform. Raise the platform to the vehicle floor loading position, stow the lift, deploy the lift and lower the platform to the ground level loading position 3,900 times.
S7.10.5.3 Perform the test sequence specified in S7.10.5.1 and S7.10.5.2 two times.
S7.10.6 Private use lifts: Using the lift controls specified in S6.7.2, perform the operation specified in S7.10.6.1 through S7.10.6.3 in the order they are given. Private use lifts that manually stow (fold) and deploy (unfold) are not required to perform the stow and deploy portions of the tests.
S7.10.6.1 Raise and lower the platform through the range of passenger operation 1,100 times.
S7.10.6.2 Remove the test pallet from the platform. Raise the platform to the vehicle floor loading position, stow the lift, deploy the lift and lower the platform to the ground level loading position 1,100 times.
S7.10.6.3 Perform the test sequence specified in S7.10.6.1 and S7.10.6.2 two times.
S7.11 Static load test II - proof load.
S7.11.1 Perform the test procedures specified in S7.11.2 through S7.11.5 and determine compliance with S6.5.2.
S7.11.2 Place the platform at the vehicle floor level loading position, center three times the standard load, including the test pallet, on the platform surface. Fully place the pallet on the platform within 1 minute of beginning to place it.
S7.11.3 Two minutes after fully placing the loaded test pallet on the platform surface, remove the loaded test pallet and examine the platform lift and vehicle for separation, fracture or breakage.
S7.11.4 After completing the static load test specified in S7.11.2 through S7.11.4, repeat Static Load Test I specified in S7.9.
S7.12 Handrail test.
S7.12.1 To determine compliance with S6.4.9.7, apply 4.4 N (1 lbf) through an area of 1290 mm2 (2 in2) in any direction at any point on the handrail in order to remove any looseness or slack from the handrail structure. Use this position of the handrail relative to the platform as the reference point for the measurement of handrail displacement. Apply 445 N (100 lbf) through an area of 1290 mm2 (2 in2) in a direction and location opposite to that of the 4.4 N (1 lbf). Attain the force within 1 minute after beginning to apply it. Five seconds after attaining the force, measure the amount of displacement of the handrail relative to the reference point, and measure the distance between the outside of the handrail and the nearest portion of the vehicle. Release the 445 N (100 lbf) and reapply the 4.4 N (1 lbf) in the direction and location that it was first applied. Five seconds after attaining the force, measure the position of the handrail with respect to the reference point to determine if there is any permanent deformation of the handrail relative to the platform.
S7.12.2 To determine compliance with S6.4.9.8, apply 4.4 N (1 lbf) through an area of 1,290 mm2 (2 in2) in any direction at any point on the handrail in order to remove any looseness or slack from the handrail structure. Use this position of the handrail relative to the platform as the reference point for the measurement of handrail displacement. Apply 1,112 N (250 lbf) through an area of 1,290 mm2 (2 in2) in a direction and location opposite to that of the 1 4.4 N (1 lbf). Attain the force within 1 minute after beginning to apply it. Five seconds after attaining the force, measure the amount of displacement of the handrail relative to the reference point. Maintain the force for two minutes. Release the force and inspect the handrail for cracking, separations or fractures.
S7.13 Wheelchair retention device overload test.
S7.13.1 Perform the test procedures as specified in S7.13.2 through S7.13.5 to determine compliance with S6.4.7.3.
S7.13.2 Position the platform surface 90 mm ±10 mm (3.5 in ±0.4 in) above the ground level loading position. Apply 7,117 N (1,600 lbf) to the wheelchair retention device in a direction parallel to both the platform lift and platform reference planes. Attain the force within 1 minute after beginning to apply it.
S7.13.3 For a wheelchair retention device that is in the form of an outer barrier, apply the force through a rectangular area with a height of 25 mm (1 in) and a width spanning the entire barrier. Distribute the force evenly about an axis 64 mm (2.5 in) above the platform reference plane. If the bottom edge of the outer barrier falls 50 mm (2 in) or more above the platform reference plane, distribute the force about an axis 13 mm (0.5 in) above the bottom edge of the barrier.
S7.13.4 For a wheelchair retention device other than an outer barrier, place the test device specified in S7.1.2 on the lift platform with its plane of symmetry coincident with the lift reference plane and directed such that forward motion is impeded by the wheelchair retention device. Move the test device forward until it contacts the wheelchair retention device. Remove the test device from the platform. Apply the force specified in S7.13.2 distributed evenly at all areas of the wheelchair retention device that made contact with the test device when it was moved forward. Attain the force within 1 minute after beginning to apply it.
S7.13.5 After maintaining the force for two minutes, remove it and examine the wheelchair retention device for separation, fracture or breakage.
S7.14 Static load test III - ultimate load.
S7.14.1 Perform the test procedures as specified in S7.14.2 through S7.14.4 to determine compliance with S6.5.3.
S7.14.2 Reinforce the vehicle structure where the lift is attached such that it is rigid and will not deform, break or separate during application of the load specified in S7.14.3 or remove the platform lift from the vehicle and install it on a test jig that is rigid and will not deform, break or separate during application of the load specified in S7.14.3.
S7.14.3 When the platform is at the vehicle floor loading position, center four times the standard load, including the test pallet, on the platform surface. Fully place the pallet on the platform within 1 minute of beginning to place it.
[67 FR 79439, Dec. 27, 2002, as amended at 69 FR 58852, Oct. 1, 2004; 69 FR 76870, Dec. 23, 2004; 77 FR 769, Jan. 6, 2012; 77 FR 20567, Apr. 5, 2012]